What Is a Decentralized Exchange?
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a platform for swapping cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Unlike traditional exchanges, where all transactions go through a centralized system, a DEX allows users to trade directly using their own crypto wallets. This makes the process more secure and private since no one else has control over your assets.
How Does a Decentralized Exchange Work?
A decentralized exchange (DEX) operates on blockchain technology and smart contracts - program code that automatically executes trade conditions without intermediaries or human involvement. When a user wants to swap one cryptocurrency for another, the smart contract verifies the conditions and completes the exchange if everything matches. This approach ensures transparency and security by eliminating intermediaries and manual processing. Depending on how they function, there are different types of DEX, which we will explore next.
Types of Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs use different methods for trading and processing transactions. Based on this, they can be divided into three main categories: order book exchanges, automated market makers (AMMs), and DEX aggregators.
Order Book Exchange
These exchanges operate based on an order book - a list of buy and sell orders for an asset. Users set the price at which they are willing to buy or sell, and the exchange automatically matches orders and executes trades.
Order book exchanges can be categorized into on-chain and off-chain models, depending on where the order data is stored and processed.
On-Chain Order Book: All orders are recorded directly on the blockchain using smart contracts, ensuring transparency and security. However, this can make trades slower and more expensive, as each order incurs a gas fee.
Off-Chain Order Book: Orders are created and stored outside the blockchain, while only the final trades are recorded on-chain. This speeds up trading and lowers fees but requires trust in the operators managing the order book.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Instead of an order book, AMM-based exchanges use liquidity pools - reserves of tokens that users can swap instantly. Each trading pair consists of two tokens (e.g., ETH and USDT), and their price changes dynamically: the more one token is bought, the higher its price becomes.
To ensure liquidity is always available, liquidity providers (LPs) deposit both tokens into the pool. In return, they receive a share of the trading fees. However, if token prices change, LPs may experience impermanent loss - this happens when the profit from providing liquidity is lower than simply holding the tokens in a wallet. At the same time, the more liquidity in the pool, the less large trades impact token prices, making swaps more predictable and reducing slippage (the difference between the expected and actual trade price).
Popular DEXs Using AMM:
-
Uniswap – the leading decentralized exchange on the Ethereum blockchain, supporting thousands of ERC-20 tokens.
-
PancakeSwap – a decentralized exchange on Binance Smart Chain (BSC). Known for its wide selection of BEP-20 tokens, user-friendly interface, lower fees, and fast transaction processing.
-
THORChain - a decentralized cross-chain liquidity protocol that allows users to swap native assets between different blockchains without wrapped assets (tokens that are pegged to an original asset but operate on a different network). For example, users can swap BTC for ETH without needing a centralized exchange.
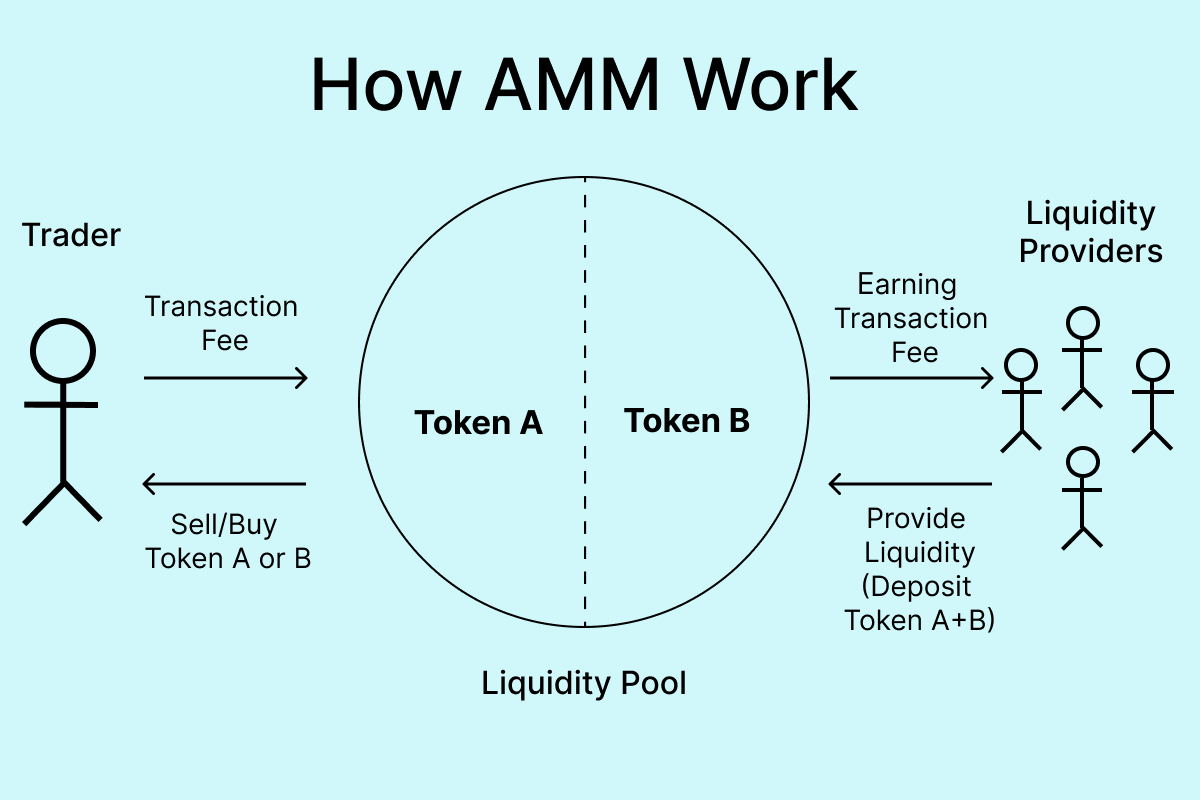 How automated market maker works
How automated market maker works
DEX Aggregators
DEX aggregators help users find the best swap rates by combining liquidity from multiple decentralized exchanges. Instead of manually checking prices on different platforms, these aggregators split and route trades across several DEXs to find the most efficient path. For example, Jupiter is the largest aggregator on the Solana network. It finds the best rates for users, making it easy to swap SPL tokens.
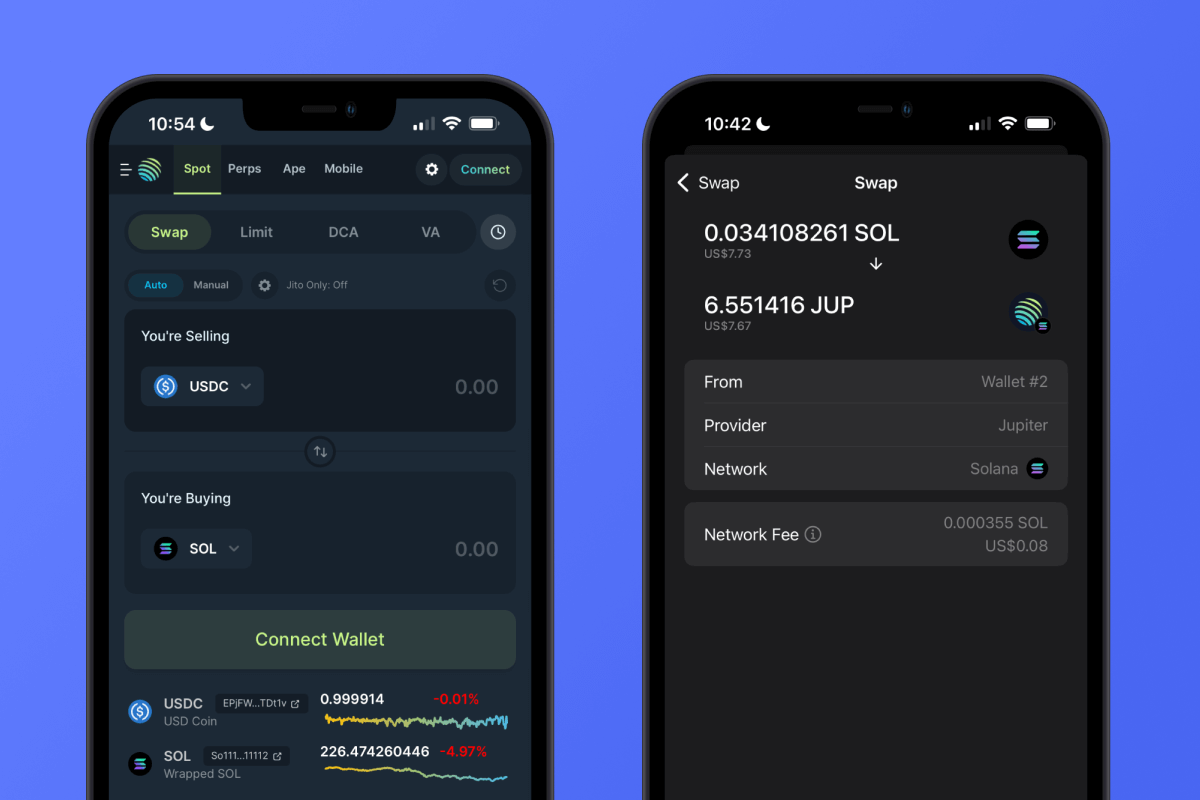 Automatic swap of Solana to SPL tokens via Jupiter. Source: Gem Wallet
Automatic swap of Solana to SPL tokens via Jupiter. Source: Gem Wallet
Advantages of Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) Over Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Unlike decentralized exchanges (DEX), centralized exchanges (CEX) manage user assets and process trades through their own servers. This creates reliance on the platform and limits users’ control over their holdings.
Decentralized exchanges solve these issues by allowing direct trading. Here are their key advantages:
-
Security: On DEX, assets remain in personal wallets instead of being stored on the platform, eliminating the risk of exchange hacks. CEX are frequent targets of cyberattacks, leading to potential asset loss for users.
-
Control Over Assets: With DEX, users trade directly from their self-custody wallets. Gem Wallet allows users to connect to decentralized exchanges and swap assets without sharing private keys. Unlike CEX, DEX prevent asset freezes and give users full control over their holdings.
-
Anonymity and No KYC: DEX do not require identity verification (KYC), whereas CEX ask for personal information.
-
Transparency: All transactions on DEX are recorded on the blockchain and can be verified at any time. On CEX, trades happen within closed systems, requiring users to trust the platform.
-
Access to a Wide Range of Tokens: DEX often list new and rare tokens before they appear on centralized exchanges.
-
Borderless Trading: Many CEX restrict access to certain tokens due to regional regulations, limiting users in some countries. DEX are borderless, allowing anyone with an internet connection to trade without geographic restrictions.
Although DEX offer greater security, privacy, and control, they also have some drawbacks, such as higher fees due to network costs and a sometimes more complex user interface. Additionally, transactions on DEX can take longer to complete, especially during network congestion. Choosing between a DEX and a CEX depends on what matters most to you - managing your assets independently, staying anonymous, or having more convenience and speed.
How to Get Started With DEX
You don’t need to register or provide an email to use a DEX - all you need is a wallet that supports smart contracts on the exchange’s network.
Set Up a Wallet
Download a wallet in just a few clicks for iOS or Android from the official website or app store. Follow the setup instructions and write down your secret recovery phrase (a set of words that lets you restore your wallet) in a safe place. Never share it with anyone!
Obtain Tokens
To swap tokens or pay transaction fees in the selected network, you’ll need some crypto in your wallet. You can receive tokens from friends, transfer from an exchange, or purchase crypto directly in the wallet using a credit card. This is a quick and convenient way to avoid mistakes when entering addresses.
Swap Tokens
Once you have crypto in your wallet, choose the token pair you want to swap and enter the amount. Then, click “Swap” - you don’t need to manually select a platform, Gem will automatically detect the network and select the best protocol, whether it’s Uniswap, PancakeSwap, THORChain, or others. You can swap tokens on DEX through a website, but it’s more convenient inside the wallet - everything you need is readily available, and the system automatically selects the best swap conditions for you.