The world of finance, business, and technology is rapidly changing thanks to blockchain. It makes systems more transparent, secure, and automates many processes. However, there is a catch: blockchain cannot independently access data from the outside world. For example, if you need to check the exchange rate of the dollar or the results of a sports match, it won’t be able to do that. This is where Chainlink comes in to help.
What Is the Chainlink Network?
Chainlink Network is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data, allowing blockchains to access reliable external information and interact with other systems. Although it was initially launched on Ethereum, Chainlink is designed to work with any blockchain that supports smart contracts. Its native token, LINK, is used to pay for services within the oracle network.
The project is open-source, enabling developers to explore its architecture and contribute to its growth. Today, over 2,000 projects use Chainlink to access trusted data, and its infrastructure continues to expand, integrating with new blockchains and protocols to improve decentralized applications.
Smart contract – a program that runs on a blockchain and automatically executes predefined conditions, such as making a payment when an agreement is fulfilled.
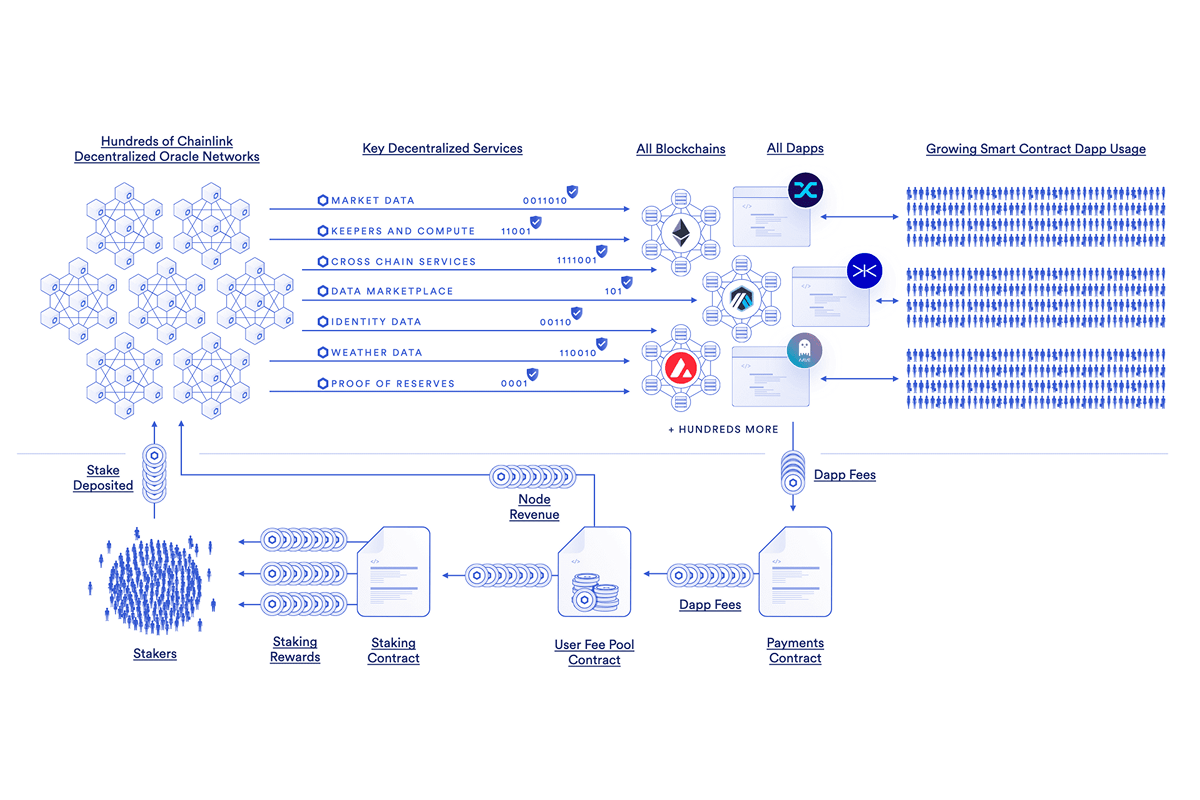 Chainlink’s economic model. Source: chain.link
Chainlink’s economic model. Source: chain.link
What Is an Oracle?
An oracle is a third-party service used to request, verify, and authenticate external data sources before transmitting the information to smart contracts. However, the problem with traditional oracles is that they are centralized, meaning they can be hacked or manipulated. If a single data provider submits false information, the smart contract may execute incorrect conditions. This risk is known as the oracle problem, and it limits the potential applications of blockchain technology.
How Does Chainlink Solve the Oracle Problem?
To solve the oracle problem, Chainlink has created a decentralized network that does not rely on a single centralized source of information. Instead, Chainlink uses a network of node operators on Ethereum. These nodes verify data before sending it to smart contracts, and a reputation system evaluates their reliability based on factors like uptime, response speed, and the number of successfully completed requests. This ensures the accuracy and security of the data used in the blockchain.
Key Features of Chainlink
What makes Chainlink unique among other oracles? Here are the key features that set Chainlink apart:
-
Decentralized Oracle Network: Chainlink does not rely on a single data source but gathers information from multiple independent nodes. This reduces the risk of manipulation and increases reliability.
-
Support for Multiple Blockchains: Originally built for Ethereum, Chainlink now supports many blockchains, including Solana, Avalanche, BNB Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism, providing a universal infrastructure for data transfer.
-
Security Through Crypto-Economic Incentives: Node operators stake LINK tokens as collateral, which motivates them to provide accurate data. If they act dishonestly, they risk losing their staked tokens.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Chainlink can be customized for various use cases, from fetching asset prices in DeFi to supplying data for insurance contracts, gaming applications, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
-
Protection Against Attacks: A data verification and aggregation mechanism reduces the risk of manipulation, while decentralization makes the network more resistant to hacks or failures.
LINK: The Native Token of Chainlink
LINK is the native token of the Chainlink ecosystem, issued on the Ethereum blockchain under the ERC-20 standard. Its maximum supply is 1 billion tokens, with 35% sold during the ICO in 2017.
The main role of LINK is to power the network. It is used to pay for oracle services, where node operators receive rewards for providing data. LINK also plays an important role in staking: node operators must lock up tokens as collateral, which encourages them to act honestly and helps secure the network. Additionally, LINK holders participate in network governance by voting on key changes and project developments.
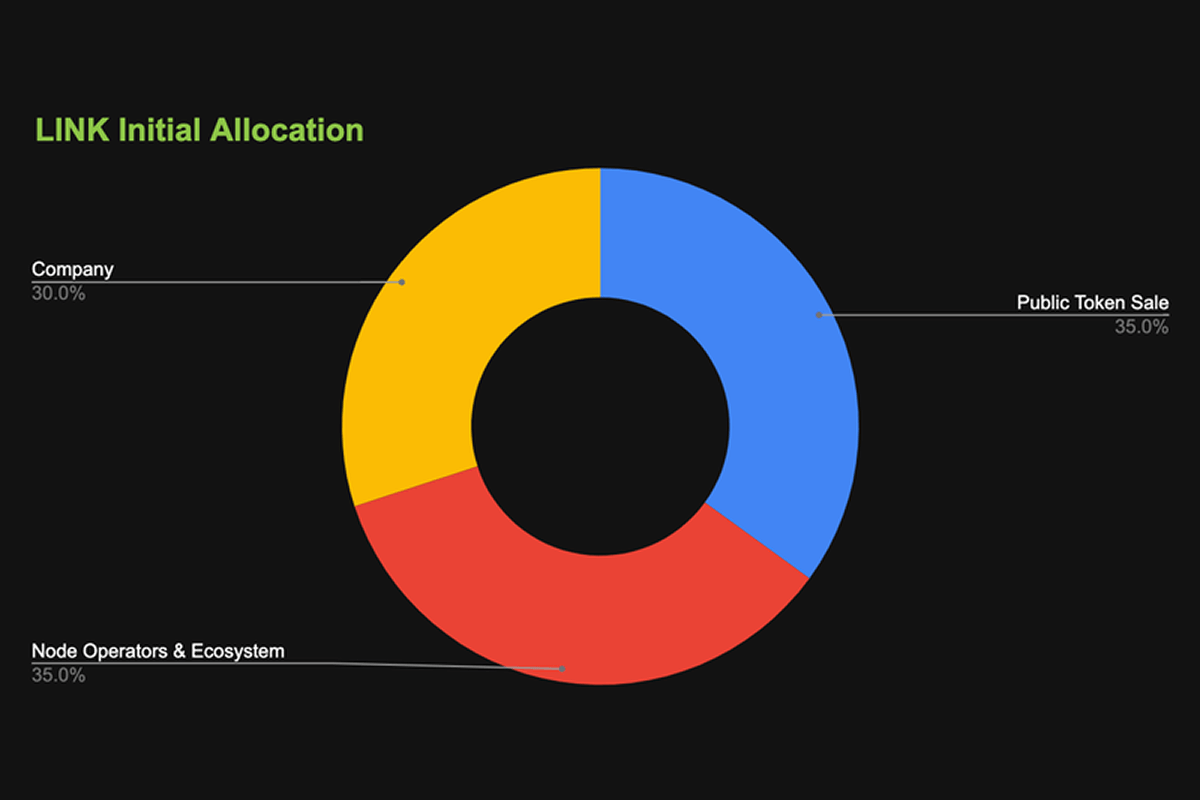 LINK Initial Token Allocation. Source: coingecko.com
LINK Initial Token Allocation. Source: coingecko.com
Use Cases of Chainlink
Chainlink is used in various industries, making blockchain more functional:
-
Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to real-world assets like the US dollar, gold, or other cryptocurrencies. To maintain this peg, they need accurate price data. Chainlink provides decentralized price oracles that track market prices in real time, helping stablecoins like DAI and TUSD stay stable.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Chainlink provides reliable data on prices, liquidity, and interest rates, helping DeFi protocols operate without manipulation risks. For example, the Aave platform uses Chainlink oracles to determine the value of collateral assets, ensuring the stability of its lending system.
-
Random Number Generation (VRF): Chainlink VRF is used in blockchain games and NFTs to fairly distribute items and conduct auctions.
-
Wrapped Tokens Reserve Monitoring: Chainlink enables the tracking of wrapped tokens’ reserves, providing smart contracts with real-time data on their backing. This ensures transparency and reliability for cross-chain assets like WBTC, helping to prevent the risk of under-collateralization.
-
Integration With Traditional Payment Systems: Chainlink allows blockchains to connect with banking systems, APIs, and services like PayPal and SWIFT.
-
Cross-Chain Interoperability (CCIP): The Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enables the transfer of assets and data between different blockchains.