
What Is Bitcoin Blockchain?
The Bitcoin blockchain is the backbone of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, representing the first-ever implementation of blockchain technology. It functions as a public ledger, transparently documenting every Bitcoin transaction. This blockchain set the stage for all subsequent blockchain technologies, leading in both market capitalization and mass adoption. While it may lack some functionalities of modern blockchains, its robust community support and unparalleled trust factor make it the foremost blockchain in the digital world.
Bitcoin vs Other Blockchains
Bitcoin is quite similar to other blockchains, as it is the original and foundational cryptocurrency. Other blockchains primarily enhance and perfect the technology established by Satoshi Nakamoto, reflecting a natural evolution of the technology. The main difference between Bitcoin and other blockchains is its immense trust and proven reliability. There is no other blockchain so broadly used as a payment method, with security backed by a capitalization close to 1 trillion dollars.
Let’s examine how the Bitcoin blockchain works - this will give you a clear understanding of the basic operations of other blockchains, without focusing on their unique modifications and improvements.
Bitcoin vs Banking
Bitcoin differs from traditional banking by publicly announcing transactions while keeping the involved parties anonymous. Unlike the banking model, which restricts information access to maintain privacy, Bitcoin ensures privacy through anonymous public keys. This means the public can see the transaction amounts but cannot identify who is involved. This approach resembles stock exchanges, where trade sizes and times are public but trader identities are not. This contrast highlights Bitcoin’s unique balance of transparency and privacy.
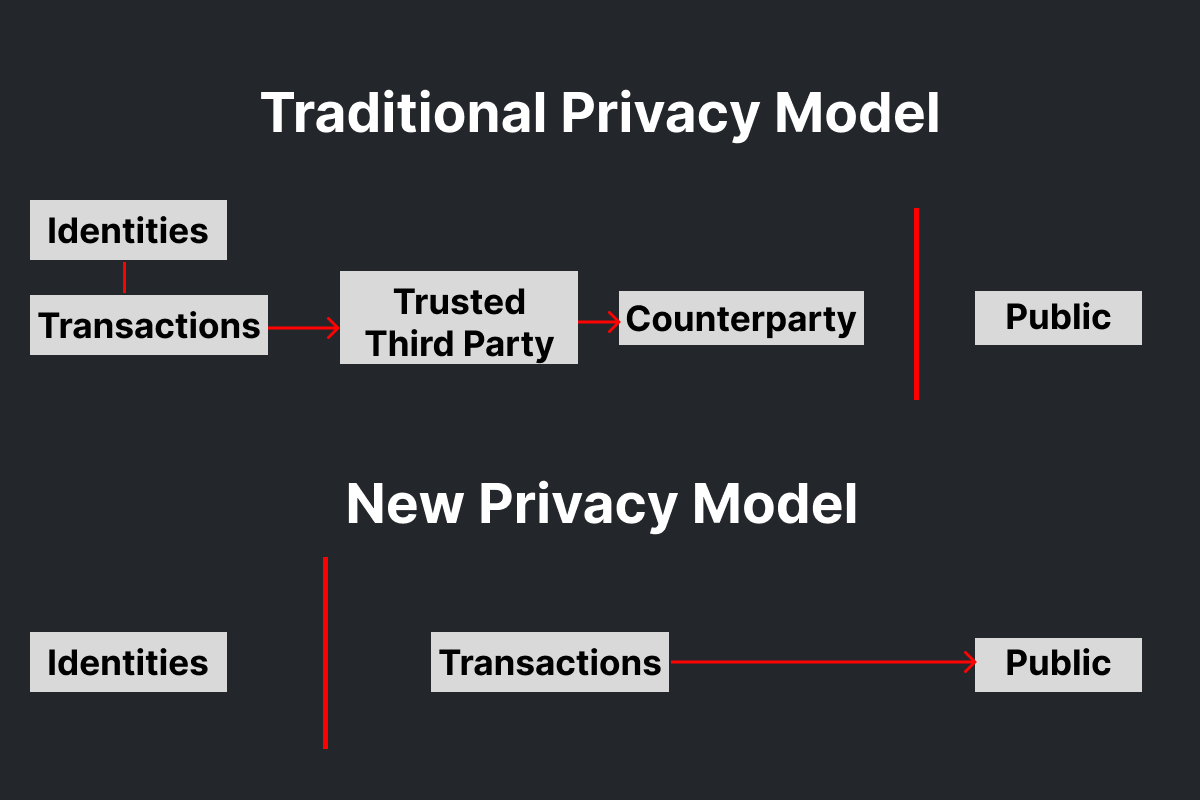 Bitcoin Privacy Model. Source: bitcoin white paper
Bitcoin Privacy Model. Source: bitcoin white paper
How Does Bitcoin Work?
At its core, the Bitcoin blockchain is a vast, public ledger where all transaction records are stored. In the Bitcoin network, clients, also known as addresses, can initiate the addition of records to this ledger by conducting transfers. Each transaction is verified and secured through a process called mining, ensuring the integrity and decentralization of the Bitcoin system. This transparent and secure mechanism is what distinguishes Bitcoin from traditional financial systems, offering a new paradigm in digital currency management.
Bitcoin Blockchain Roles
Let’s take a look at the three key roles in the operation of a blockchain.
-
Users: These are individuals or organizations that use Bitcoin for transactions. They send and receive bitcoins using their Bitcoin addresses and cryptographic keys.
-
Miners: These are specialized network participants who use the power of their computers to process transactions and form new blocks in the blockchain. For their work, miners receive rewards in the form of new bitcoins (a process known as mining) and transaction fees.
-
Public Nodes: These are network nodes that support the Bitcoin blockchain, storing a full copy of the block chain and spreading information about transactions across the network. Nodes play a key role in maintaining the transparency and security of the network, verifying blocks and transactions according to the consensus rules of Bitcoin.
What Are Blockchain Blocks and Mining?
Blockchain blocks are individual sections of the digital ledger, where each block contains a group of Bitcoin transactions. These blocks are linked in a chain, creating a permanent and tamper-proof record of all transactions. Mining is the process where miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. Successfully solving these puzzles allows them to add a new block to the blockchain and, in return, they are rewarded with newly created bitcoins and transaction fees. This process not only generates new bitcoins but also secures the network and verifies transactions, making the Bitcoin blockchain a decentralized and trustworthy system.
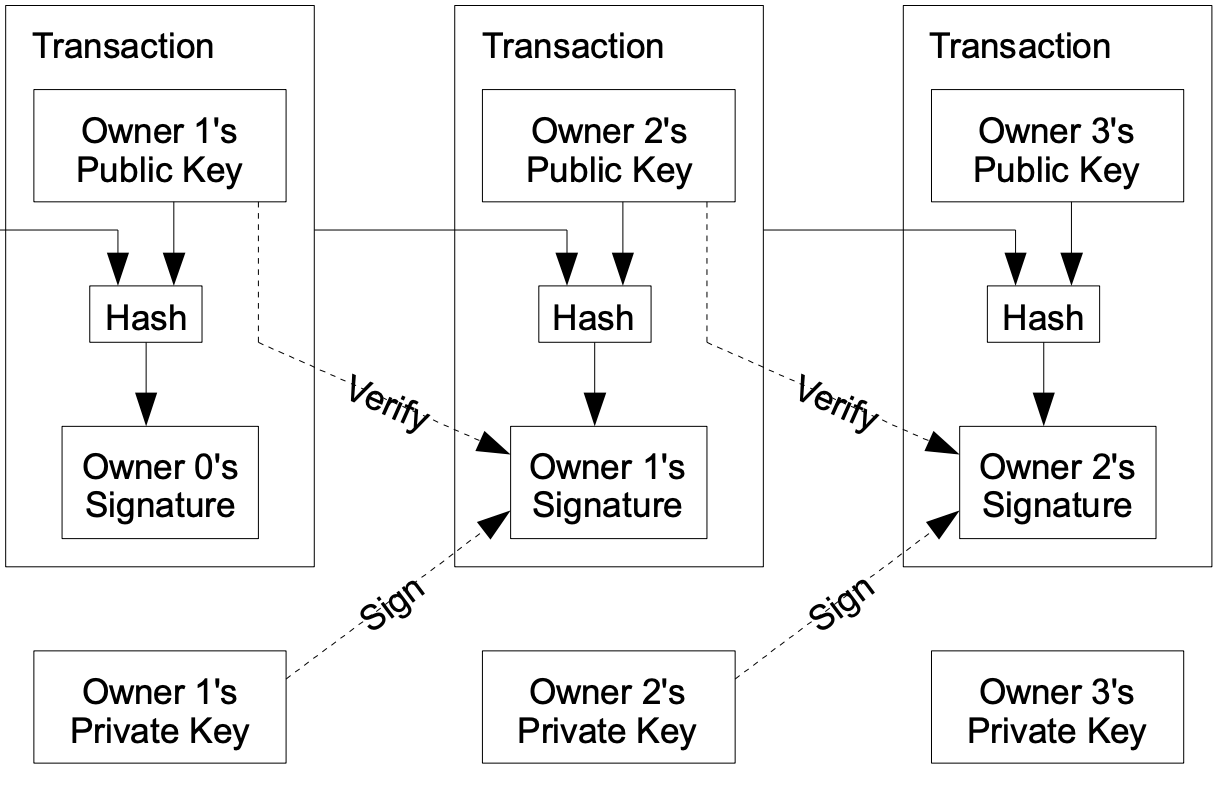 Blockchain Transactions Scheme. Source: bitcoin white paper
Blockchain Transactions Scheme. Source: bitcoin white paper
Bitcoin Halving, Limited Supply, Deflationary Model - Driving High Demand and Low Supply
-
Bitcoin Halving - You’ve likely heard this term, but what does it mean for the Bitcoin blockchain? When miners create a new block in the network, they receive a reward. Halving refers to the reduction of this reward by half, which, in the long term, means miners will earn fewer bitcoins. Consequently, the market supply will decrease, creating a scarcity of coins.
-
Limited Supply - The Bitcoin blockchain is capped at a maximum number of coins, protecting investors from inflation. This fixed supply limit is a key feature that differentiates Bitcoin from traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed without limit by governments.
-
Deflationary Model - Unlike some newer blockchains that utilize coin burning mechanisms, Bitcoin experiences a “natural coin burn.” Stories of lost laptops with thousands of bitcoins on hard drives that have been misplaced or discarded are well-known. Over time, a portion of bitcoins are lost due to human errors or accidents, effectively reducing the market supply.
Together, these three elements act as strong drivers of price growth. While this doesn’t guarantee that the price will only increase, they represent a powerful factor that should be considered when evaluating long-term investments in Bitcoin. These mechanisms ensure that Bitcoin remains a scarce digital asset, making it more valuable over time as the supply becomes more limited.
BTC: Digital Gold
When people talk about Bitcoin or BTC, they are usually referring to the Bitcoin blockchain’s coin, BTC. This makes sense, as the Bitcoin blockchain itself represents and reflects the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem. Its main mission is storage, investment, and payments, which are directly related to the BTC coin itself.
Tokenomics of BTC
-
Total Supply: 21,000,000 BTC.
-
Circulating Supply: 19,594,156 BTC.
Uses of BTC
-
Transaction Fees: If you decide to send your BTC to an exchange, friends, or to a backup address, you will need to spend a certain amount of BTC on transaction fees. For smaller transfers, the fee can be relatively high compared to the amount being sent. Therefore, it’s better to optimize your payments by transferring larger amounts in fewer transactions. This approach not only reduces the total fees paid but also contributes to the efficiency of the Bitcoin network by decreasing congestion and the number of transactions that need to be processed.
-
Investment: Bitcoin is often aptly called digital gold. If you believe in the potential of cryptocurrency assets and see a future in them, then Bitcoin should be a key component of your cryptocurrency portfolio. As the coin with the highest trust and user adoption, Bitcoin’s value directly reflects the development of the crypto market. Additionally, Bitcoin’s limited supply, coupled with growing demand, acts as a catalyst for the appreciation of your investment. The security of your funds on the Bitcoin blockchain is best illustrated by its long history of existence, during which there has been nothing to cast doubt on its security and reliability. This history underlines Bitcoin’s position not just as a pioneering cryptocurrency but also as a relatively safe and stable digital asset in the often-volatile crypto market.
-
Payment Method: Despite relatively high transaction fees and somewhat lengthy processing times, BTC remains a favorite for cryptocurrency payments. Its widespread popularity and the trust users place in Bitcoin, coupled with its security, reliability, and a degree of privacy, make it a versatile payment tool. Furthermore, the ability to directly purchase Bitcoin from a wallet using a credit card greatly simplifies and speeds up the process, enhancing its convenience for users.

